How Bitcoin can help secure proof-of-stake blockchain protocols
The proof-of-work consensus mechanism of Bitcoin (BTC) could become a useful means of securing a variety of proof-of-stake (PoS) smart contract blockchain protocols thanks to efforts from a Stanford University professor.
David Tse and his research team are driving the use of the preeminent cryptocurrency to provide added security to PoS networks. Tse’s proprietary Babylon blockchain aims to use Bitcoin to bolster network security and incentivize BTC holders to participate in what is ostensibly a new approach allowing staking of Bitcoin on proof-of-stake chains.
In an interview with Cointelegraph, Tse outlined how Babylon uses the Bitcoin scripting language to connect a PoS-based slashing mechanism to the Bitcoin network. This allows for the creation of smart contracts that are able to set specific spending conditions:
Tse said that Babylon’s BTC staking protocol enables BTC to be used to secure its network without having to alter or fork the Bitcoin protocol. This also allows BTC holders the ability to earn rewards for contributing to the security of PoS network’s by staking their BTC.
The Stanford professor also added that the simplicity of the approach also maximizes the security of blockchains by avoiding potential vulnerabilities associated with cross-chain bridges. As Cointelegraph has previously explored, cross-chain hacks and exploits have been rife, leading to over $2 billion being fleeced over the past year.
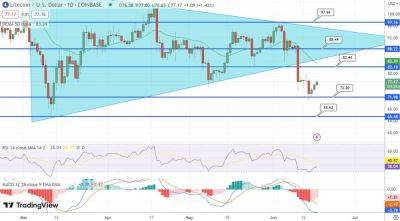
Bitcoin remains unrivaled as the largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization and continues to operate on the original specifications set out by its pseudonymous creator Satoshi Nakamoto.
Nevertheless the ecosystem has seen renewed interest and growth with the inception of Bitcoin Ordinals, which allow users
Read more on cointelegraph.com