Bitcoin’s Lightning Network is growing, but there are still three major challenges
The Lightning Network is a second-layer solution built on top of the Bitcoin (BTC) blockchain and its primary objective is to address the Bitcoin network’s scalability issues. It also allows for faster and cheaper transactions by facilitating off-chain payments through a network of payment channels.
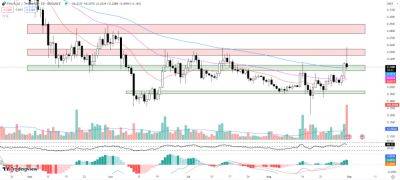
The Lightning Network has gained traction since its launch in 2018, hitting a total value locked (TVL) of $140 million, but this is relatively small compared to Bitcoin's $580 billion market capitalization. However, this oversimplification disregards that this scaling solution focuses on instant transactions, not lending, yield farms or other activities that require staking.
Additionally, the number of nodes grew by a mere 6% since June 2022. This suggests that there are significant reasons why it has not achieved mainstream adoption. Let’s take a look at a few of the factors influencing Lightning Network growth.
If a Lightning Network user wishes to make a payment that exceeds their channel balance, they must find a well-funded node with a direct channel to the recipient to facilitate the transaction. This process can be challenging and time-consuming, especially if the recipient is not well-connected within the Lightning Network.
Channel balancing requires users to manage the funds in their channels effectively. Rebalancing is automatic when using apps like the Phoenix or Breeze, but it adds complexity for mid level users relying on their own nodes. According to Viktor Bunin, protocol specialist at Coinbase Cloud:
Besides the issue of optimizing the channels’ funding, there is also the associated costs of opening and closing channels as it requires an on-chain transaction. That can create serious issues if the median fee
Read more on cointelegraph.com